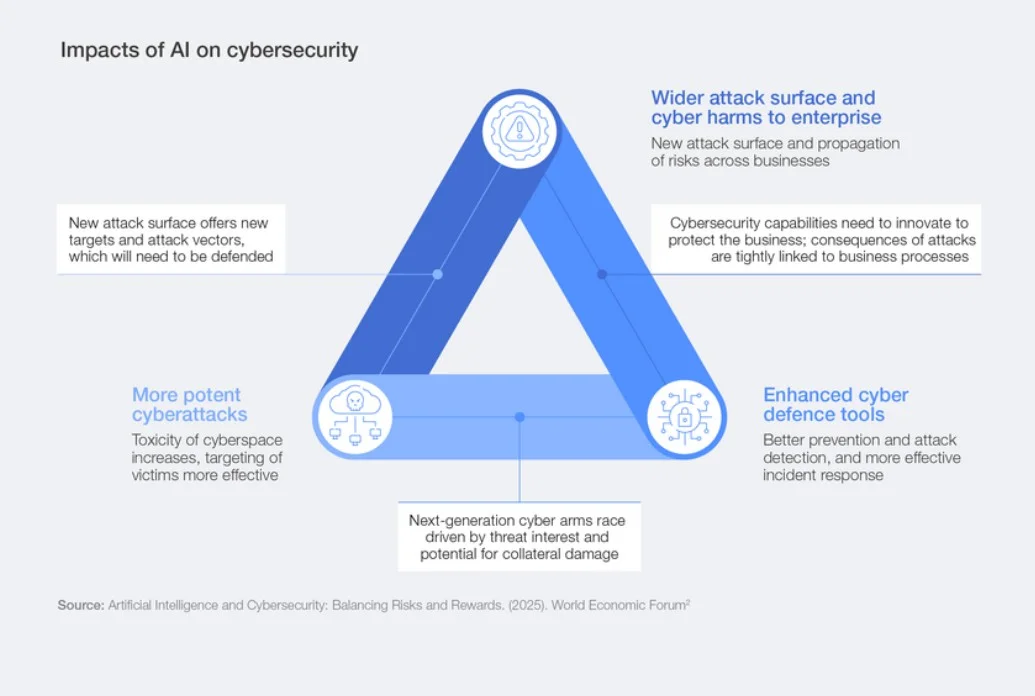
The World Economic Forum's Global Cybersecurity Outlook report indicates that by 2026, AI will be a major catalyst for change in cybersecurity. A survey encompassing over 800 cybersecurity leaders shows that a significant 94% are aware of AI-related security concerns, highlighting a shift in focus for many CEOs and Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs).
While there is a noted transition among CEOs towards prioritizing cyber-enabled fraud over ransomware, CISOs continue to emphasize the importance of ransomware and the resilience of supply chains. This difference in focus underscores the contrasting priorities between executive management and security teams. The report reveals that 87% of participants view AI vulnerabilities as the most rapidly escalating cyber threat.
Concerns about cyber-enabled fraud, phishing, and supply chain issues were expressed by over half of the respondents, with insider threats and denial of service (DoS) attacks recognized by approximately 30% as rising threats. Additionally, the report noted that the percentage of organizations performing security assessments on AI tools has surged from 37% in 2025 to 64% in 2026. Yet, 36% still lack a formal process for evaluating AI security, suggesting ongoing vulnerabilities amid increasing AI utilization.
To strengthen AI security, the report advocates for measures such as protecting training data, integrating security in AI development, and employing robust authentication and encryption techniques. Furthermore, 77% of organizations have started using AI in their cybersecurity strategies, with specific enhancements in phishing detection, intrusion response, and user behavior analytics.